Information About Diabetes Mellitus, Causes, Symptoms And How To Treat Diabetes
 |
| Diabetes Melitus |
Symptoms Frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger, diabetes is a result of either the pancreas not producing enough insulin or cells in the body not responding properly on the insulin produced. There are three main forms of diabetes mellitus:
Type 1 DM comes from the pancreas's failure to produce enough insulin. This form once was termed as "insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
Several other indicators can mark the start diabetes whilst they aren't specific towards the disease. In addition towards the known ones above, they include blurry vision, headache, fatigue, slow healing of cuts, and itchy skin. Prolonged high blood glucose may cause glucose absorption inside lens in the eye, which ends up in adjustments to its shape, causing vision changes. A number of skin rashes that can exist in diabetes are collectively generally known as diabetic dermadromes
The classic signs and symptoms of untreated diabetes are weight reduction, polyuria (increased urination), polydipsia (increased thirst), and polyphagia (increased hunger).[19] Symptoms may develop rapidly (weeks or months) in type 1 DM, while they usually develop much more slowly and might be subtle or absent in type 2 DM.
Low blood sugar levels are common in persons with type 1 and type 2 DM. Most cases are mild and so are not considered medical emergencies. Effects ranges from feelings of unease, sweating, trembling, and increased appetite in mild cases to more serious issues like confusion, adjustments to behavior such as aggressiveness, seizures, unconsciousness, and (rarely) permanent brain damage or death in severe cases. Moderate hypoglycemia may be mistaken for drunkenness, rapid breathing and sweating, cold, pale skin are manifestation of hypoglycemia and not definitive. Mild to moderate cases are self-treated by consuming or drinking something full of sugar. Severe cases can result in unconsciousness and must be helped by intravenous glucose or injections with glucagon.
People (usually with type 1 DM) might also experience episodes of diabetic ketoacidosis, a metabolic disturbance characterized by nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain, the give an impression of acetone about the breath, yoga breathing referred to as Kussmaul breathing, along with severe cases a low a higher level consciousness
 |
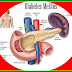
| Diabetes Melitus, source : Wikipedia |
A positive result, even without the unequivocal high blood sugar, must be confirmed by way of a repeat associated with a with the above methods with a different day. It is better than measure a fasting glucose level because from the simplicity of measurement along with the time and effort commitment of formal glucose tolerance testing, which takes 2 hours to perform and will be offering no prognostic advantage on the fasting test. According to the current definition, two fasting glucose measurements above 126 mg/dl (7.0 mmol/l) is regarded as diagnostic for diabetes mellitus.
Per the World Health Organization people with fasting blood sugar levels from 6.1 to six.9 mmol/l (110 to 125 mg/dl) are viewed to have impaired fasting glucose.[63] people with plasma glucose at or above 7.8 mmol/l (140 mg/dl), and not over 11.1 mmol/l (200 mg/dl), 2 hours from a 75 g oral glucose load are considered to have impaired glucose tolerance. Of these two prediabetic states, the latter particularly is often a major risk factor for progression to full-blown diabetes mellitus, in addition to cardiovascular disease. The American Diabetes Association since 2003 runs on the slightly different range for impaired fasting glucose of 5.6 to six.9 mmol/l (100 to 125 mg/dl).
The relationship between diabetes type 2 as well as the main modifiable risk factors (extra weight, unhealthy diet, physical inactivity and tobacco use) is comparable in all of the aspects of the globe. There is growing evidence that this underlying determinants of diabetes can be a reflection from the major forces driving social, economic and cultural change: globalization, urbanization, population aging, and the overall health policy environment.
There is no known protection for type 1 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes, which accounts for 85 - 90% of all cases, can often be prevented or delayed by maintaining an average body weight, engaging in physical exercise, and consuming balanced and healthy diet. Higher levels of physical exercise (more than 90 minutes every day) decrease the chance of diabetes by 28%. Dietary changes known to be effective in preventing diabetes include maintaining a diet plan abundant with grain and fiber, and choosing good fats, for example the polyunsaturated fats present in nuts, vegetable oils, and fish. Limiting sugary beverages and eating less steak along with other reasons for saturated fats can also help prevent diabetes. Tobacco smoking is additionally associated with an increased risk of diabetes and it is complications, so stop smoking is definitely an important safety measure at the same time.
All doctors advise using diet to assist lower blood sugar, but why the brand new claim so controversial may be the proven fact that the proper type of diet can in fact reverse diabetes, eliminating the necessity for drugs altogether.
Type 2 diabetes is a result of our bodies becoming resistant to the hormone insulin, resulting in a gradual rise in blood sugar. People who are overweight and not physically active will be more at an increased risk, particularly those with plenty of fat across the abdomen.
Longer term, the problem can bring about and the higher chances of cardiac arrest, kidney damage, blindness and harm to bloodstream inside the legs and feet, which may even have to be amputated.
source : wikipedia
source : wikipedia









0 comments:
Post a Comment